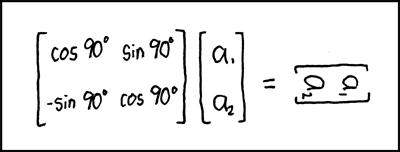|
|
1 年之前 | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .github | 1 年之前 | |
| classes | 1 年之前 | |
| examples | 1 年之前 | |
| README.md | 1 年之前 | |
| buildPhar.php | 1 年之前 | |
| composer.json | 1 年之前 | |
| infection.json.dist | 1 年之前 | |
| license.md | 1 年之前 | |
| phpstan.neon | 1 年之前 | |
README.md
PHPMatrix
PHP Class for handling Matrices
Matrix Transform
This library currently provides the following operations:
- addition
- direct sum
- subtraction
- multiplication
- division (using [A].[B]-1)
- division by
- division into
together with functions for
- adjoint
- antidiagonal
- cofactors
- determinant
- diagonal
- identity
- inverse
- minors
- trace
- transpose
- solve
Given Matrices A and B, calculate X for A.X = B
and classes for
Decomposition
- LU Decomposition with partial row pivoting,
such that [P].[A] = [L].[U] and [A] = [P]|.[L].[U]
- QR Decomposition
such that [A] = [Q].[R]
TO DO
- power() function
- Decomposition
- Cholesky Decomposition
- EigenValue Decomposition
- EigenValues
- EigenVectors
Installation
composer require markbaker/matrix:^3.0
Important BC Note
If you've previously been using procedural calls to functions and operations using this library, then from version 3.0 you should use MarkBaker/PHPMatrixFunctions instead (available on packagist as markbaker/matrix-functions).
You'll need to replace markbaker/matrixin your composer.json file with the new library, but otherwise there should be no difference in the namespacing, or in the way that you have called the Matrix functions in the past, so no actual code changes are required.
composer require markbaker/matrix-functions:^1.0
You should not reference this library (markbaker/matrix) in your composer.json, composer wil take care of that for you.
Usage
To create a new Matrix object, provide an array as the constructor argument
$grid = [
[16, 3, 2, 13],
[ 5, 10, 11, 8],
[ 9, 6, 7, 12],
[ 4, 15, 14, 1],
];
$matrix = new Matrix\Matrix($grid);
The Builder class provides helper methods for creating specific matrices, specifically an identity matrix of a specified size; or a matrix of a specified dimensions, with every cell containing a set value.
$matrix = Matrix\Builder::createFilledMatrix(1, 5, 3);
Will create a matrix of 5 rows and 3 columns, filled with a 1 in every cell; while
$matrix = Matrix\Builder::createIdentityMatrix(3);
will create a 3x3 identity matrix.
Matrix objects are immutable: whenever you call a method or pass a grid to a function that returns a matrix value, a new Matrix object will be returned, and the original will remain unchanged. This also allows you to chain multiple methods as you would for a fluent interface (as long as they are methods that will return a Matrix result).
Performing Mathematical Operations
To perform mathematical operations with Matrices, you can call the appropriate method against a matrix value, passing other values as arguments
$matrix1 = new Matrix\Matrix([
[2, 7, 6],
[9, 5, 1],
[4, 3, 8],
]);
$matrix2 = new Matrix\Matrix([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
]);
var_dump($matrix1->multiply($matrix2)->toArray());
or pass all values to the appropriate static method
$matrix1 = new Matrix\Matrix([
[2, 7, 6],
[9, 5, 1],
[4, 3, 8],
]);
$matrix2 = new Matrix\Matrix([
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
]);
var_dump(Matrix\Operations::multiply($matrix1, $matrix2)->toArray());
You can pass in the arguments as Matrix objects, or as arrays.
If you want to perform the same operation against multiple values (e.g. to add three or more matrices), then you can pass multiple arguments to any of the operations.
Using functions
When calling any of the available functions for a matrix value, you can either call the relevant method for the Matrix object
$grid = [
[16, 3, 2, 13],
[ 5, 10, 11, 8],
[ 9, 6, 7, 12],
[ 4, 15, 14, 1],
];
$matrix = new Matrix\Matrix($grid);
echo $matrix->trace();
or you can call the static method, passing the Matrix object or array as an argument
$grid = [
[16, 3, 2, 13],
[ 5, 10, 11, 8],
[ 9, 6, 7, 12],
[ 4, 15, 14, 1],
];
$matrix = new Matrix\Matrix($grid);
echo Matrix\Functions::trace($matrix);
$grid = [
[16, 3, 2, 13],
[ 5, 10, 11, 8],
[ 9, 6, 7, 12],
[ 4, 15, 14, 1],
];
echo Matrix\Functions::trace($grid);
Decomposition
The library also provides classes for matrix decomposition. You can access these using
$grid = [
[1, 2],
[3, 4],
];
$matrix = new Matrix\Matrix($grid);
$decomposition = new Matrix\Decomposition\QR($matrix);
$Q = $decomposition->getQ();
$R = $decomposition->getR();
or alternatively us the Decomposition factory, identifying which form of decomposition you want to use
$grid = [
[1, 2],
[3, 4],
];
$matrix = new Matrix\Matrix($grid);
$decomposition = Matrix\Decomposition\Decomposition::decomposition(Matrix\Decomposition\Decomposition::QR, $matrix);
$Q = $decomposition->getQ();
$R = $decomposition->getR();